Guinea Red Cross
Dates of implementation: 2019 - present (previous implementations 2017-2018)
Settings: Mixed
Context: Preparedness/ scale-up in emergencies
Data collection system: Started with KoBo reporting system and transitioned to Nyss in 2023
Partners: USAID, International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (previous partners included Danish Red Cross, American Red Cross and French Red Cross)
Guinea is a country in West Africa with a population of almost 12 million. Guinea was hit in the 2014 Ebola epidemic, recording 3,811 cases and 2,543 deaths. The epidemic – which ended in mid 2016 - highlighted and exacerbated the health and surveillance systems’ weaknesses. These include weakness of fundamental prevention, surveillance and disease control at all levels, and particularly in the community, as well as the limited geographical coverage of health care services in remote parts of Guinea.
In a bid to tackle these weaknesses, the National Health Security Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité Sanitaire or 'ANSS'), set up in 2015, developed a national Community-based Surveillance (CBS) program. A multi-stakeholder working group, which includes the Guinea Red Cross, works to harmonize their implementation of CBS, support ANSS, as well as create normative documents. In theory, each supporting partner should take care of implementing CBS in one or more prefectures in the country, based on 6 diseases of epidemic potential.
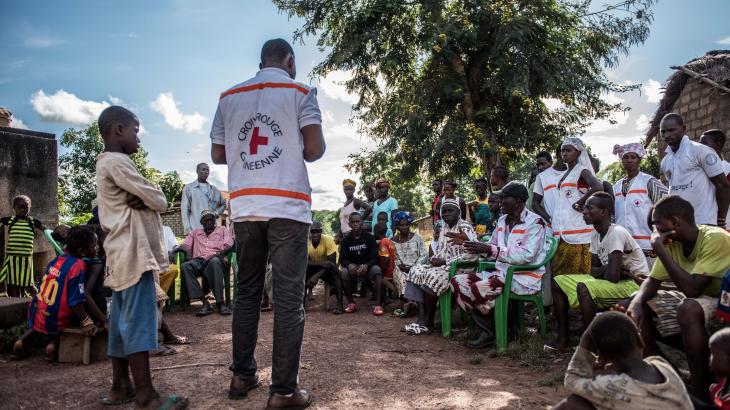
Since 2019 the Guinea Red Cross, with support from the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) and funding from USAID, has been helping communities to prepare for and prevent the spread of diseases. Volunteers in Dinguiraye, Dabola, Faranah, Kissidougou and Nzérékoré prefectures raise awareness of health risks—particularly diseases such as rabies, viral hemorrhagic fevers and yellow fever—and help people take steps to protect themselves. They actively engage in CBS to rapidly detect and report suspicious health events for a rapid response from Guinean authorities.
In Guinea, canine rabies is endemic. Statistics available from the technical services of the Ministry of Livestock and the Ministry of Health indicate that between 2018 and August 2020, 1,823 cases of dog bites were recorded for 14 cases of human rabies. These figures are underestimated due to under-reporting of bite cases.
Guinea Red Cross in action
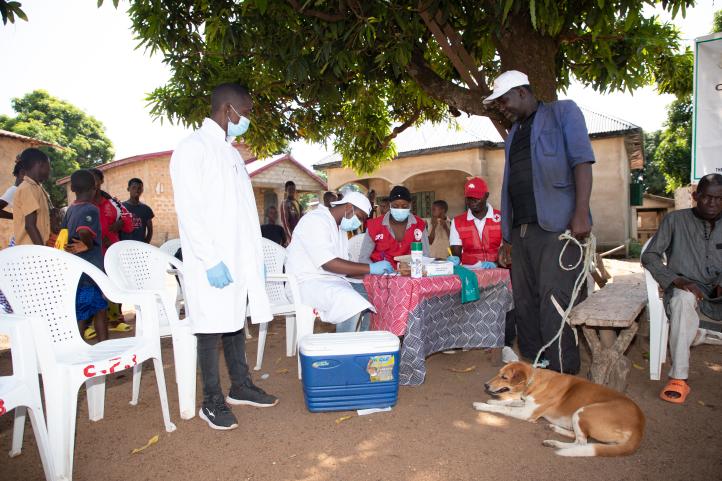
During the month of February 2022, seven cases of bites by dogs that tested positive for rabies were recorded in the district of Banian, Faranah prefecture, through the Red Cross community-based surveillance system.
This situation prompted Guinea's One Health platform to organize a rabies campaign in Bania and the surrounding sub-prefectures of Ballayah, Bambaya and Tiro. Red Cross volunteers raised awareness about rabies. Children and dog owners were given special attention because children are particularly vulnerable to dog bites and the success of the dog vaccination depends on the support of the owners.
Volunteers reached 2,490 people with rabies prevention messages and supported more than 200 dogs to be vaccinated.
RESULTS
-
Increased alerts escalated to ANSS led to rapid investigations and responses, decreasing opportunities for suspected and confirmed cases to reach outbreak thresholds.
-
17 alerts for rabies were raised in 2022 leading to rapid responses, community engagement opportunities and vaccination campaigns to improve rabies control through a One Health approach.
-
Reporting on unusual illnesses & deaths among animal populations led to case investigation by animal health authorities in >96% alerts escalated
KEY LESSONS LEARNED & RECOMMENDATIONS
- Training and Detection: Provide refresher trainings and trainings in other areas (first aid, WASH, CBHFA). Distribute image memory cards to volunteers to help them remember signs and symptoms of health risks under surveillance. Routinely test volunteers' ability to detect cases.
- Coordination and communication with ANSS: Establish a Memorandum of Understanding or other formal agreement between Guinea Red Cross and ANSS. Articulate epidemiological arguments – where appropriate, to support CBS implementation in project areas, even if not in line with national strategy. Assure a continued presence of Guinea Red Cross at key meetings in ANSS and showcase the value of the work done by Guinea Red Cross.
- Community engagement: Implement a package of activities tailored to the needs expressed by the communities when starting a CBS project (health sensitization, WASH), to promote trust, project support and sustainability.